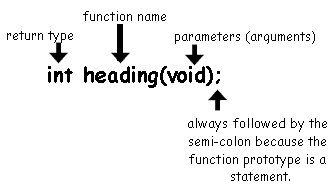
1. Declare the function. The
declaration, called the function
prototype, tells the computer the name,
return type, and parameters of the function. This statement is placed
after #include<iostream.h> (and other headers) and before
int main(void).
2. Define the function. The
function definition tells the compiler what task the function will be
performing. A function definition cannot be
called unless the function is declared. The
function prototype and the function definition must agree EXACTLY
on the return type, the name, and the parameters. The only difference
between the function prototype and the function header is a semicolon (see
diagram below). The function
definition is placed AFTER the end of the int main(void)
function.
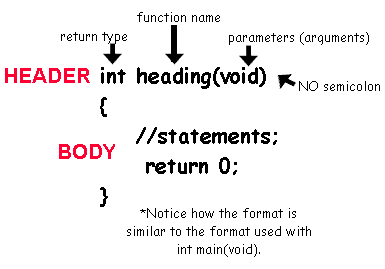
The function definition
consists of the function header
and its body.
The header
is EXACTLY like the function prototype, EXCEPT that it contains NO
terminating semicolon.
|