|

Return to Topic Menu
|
Computer Science Main Page |
MathBits.com |
Terms of Use
Logical
Operators
|
|
Run your mouse over the
panel at the left to see information about the logical operators.
|
A single
comparison in an if
statement often is not enough to determine whether data matches your
criteria. For example, you may need to check to see if a user
enters a number within a certain range. To accomplish this task, you
will need the logical operators in your
if statement.
These
logical operators which result in a TRUE/FALSE condition are also
referred to as Boolean
Operators.
|
It's
time to remember those truth tables from Mathematics! Yeek!! |
| &&
(AND) |
| |
(3 + 2 = 5)
&& (6 + 2 = 8) TRUE |
| |
(4 + 3 = 9)
&& (3 + 3 = 6) FALSE |
| |
| (OR) found above
the backslash on the keyboard |
| |
(3 + 6 = 2) || (4
+ 1 = 5) TRUE |
| |
(1 + 1 = 3) || (3
+ 3 = 9) FALSE |
| !
(NOT) |
| |
!(4 + 3 =
5) TRUE |
 |
BEWARE:
Math:
2 < x < 10
OK
Computer: if (2
< x < 10) NO!!!
The
computer will only check the
first condition 2 < x.
if ((2 < x) && (x <
10)) YES |
|
|
|
Remember DeMorgan's
Laws: |
| Mathematical Version: |
Programming Version: |
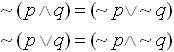 |
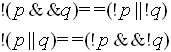 |
Equivalent statements:
if (!(num >= 0 && num <= 65))
if (num < 0 || num > 65) |
Return to Topic Menu
|
Computer Science Main Page |
MathBits.com |
Terms of Use
|